What is a Third Party
What is a Third Party?
A third party refers to an external resource that is not directly controlled or owned by the website owner. Third parties are used to provide functionality or content to your website.
Here are common examples of third parties on a website:
Advertising Networks
Advertisers or ad networks that display ads on a website. These ads are often served by third-party ad servers, and the website owner may earn revenue based on ad impressions or clicks.
Analytics Services
Services like Google Analytics or Matomo provide website owners with insights into user behaviour and traffic patterns. They might also contain features like heatmaps and surveys. These services often involve embedding tracking code provided by a third party. Websites might use tracking pixels such as LinkedIn or Facebook. These are small, often invisible graphics embedded in a web page. Marketing teams often use tracking pixels to measure the success of online advertising campaigns in getting new users to visit the website.
Social Media Widgets
These are buttons, feeds, or plugins from social media platforms (e.g., Facebook, Twitter) that allow users to share or interact with content on the website.
E-commerce Platforms
Platforms such as Shopify, WooCommerce and Magento are software solutions that allow businesses to create and manage online stores. They can facilitate the entire e-commerce process, from product listing and inventory management to payment processing and order fulfilment.
Payment Processors
These are services like PayPal or Stripe that handle online payment transactions. When a website integrates these services, users are redirected to the third-party platform to complete their transactions securely (it might also be integrated into the site itself via an iframe). You might also notice multiple payment options via multiple third parties.
Payment processors enable websites to handle payments securely it is also important to remember that the website is still responsible for ensuring customer details are secure, not just the third party!
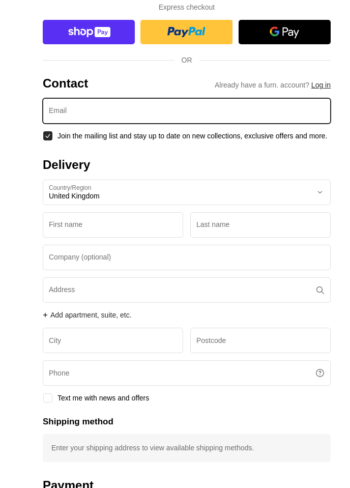
Payment pages often use multiple third-party payment services
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs like Cloudflare, Akamai, or Amazon CloudFront help deliver website content more efficiently by distributing it across multiple servers located in different geographic regions.
Widgets and Embeds
Embedded content such as YouTube videos, Google Maps, or other widgets provided by external services can be added to websites. This content is hosted and controlled by third parties.
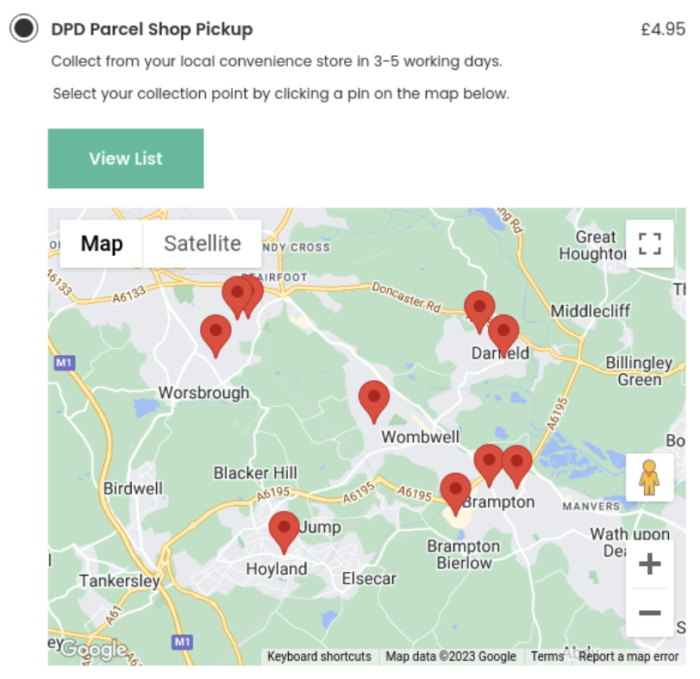
Maps can be embedded into websites
External Fonts
Fonts loaded from third-party font libraries like Google Fonts or Adobe Fonts can be used to enhance the visual design of the website.
Chat and Support Tools
Live chat services or customer support tools (e.g., Intercom, Zendesk) allow website owners to provide real-time assistance to users.
Live chat boxes are often third-party plugins that allow users to quickly get in touch with support teams.
Third Parties and Risks
This by no means covers all the possible third parties you could include on your website,
It is crucial for website owners and developers to carefully manage and evaluate the use of third-party elements to ensure they align with privacy and security standards. Additionally, too many third-party elements can affect website performance and load times.
Read More
https://www.rapidspike.com/blog/third-party-planning-be-careful-who-you-invite/